transcreation & Transadaptation
Translation moves words. Transcreation and transadaptation move meaning. In a global environment, that difference matters. To make your message work, the approach you choose is everything.
Have questions?
Get the answers you’re looking for. Contact us. No obligation.
Get In Touch
Phone: +1.833.726.8486 Helpdesk: info@santium.com
Supporting Solutions
Not just translated. made to work.
TRANSCREATION vs. TRANSADAPTATION
Some content cannot be translated word for word. Sometimes not at all.
Transcreation and transadaptation go beyond literal translation. Collectively also referred to as “cultural adaptation”, they recreate creative, branded, conceptual, and culturally nuanced content so that intent, impact, emotional resonance, and user experience are preserved (or enhanced) in the target language and cultural context.
What is transadaptation?
Transadaptation is a translation process used when the original concept is valid in the target culture, but the exact wording cannot be transferred without changing its meaning.
For example, a symptom description, instruction, or behavioral term may exist in both cultures, but the literal phrasing carries a different intensity, medical nuance, or implied assumption. If translated word-for-word, the target audience might interpret it more narrowly, more broadly, or differently than intended.
Transadaptation corrects this by modifying specific words, adjusting phrasing, clarifying implied meaning, or recalibrating tone so that the target audience understands the concept in the same way as the source audience. The underlying idea does not change, only the linguistic expression does.
In short:
The concept works but the wording must be adjusted to preserve it.
What is Transcreation?
Transcreation is a translation process that goes further; it is used when the original concept, framing, or reference does not work in the target culture at all.
This may happen when a message relies on a culturally specific metaphor, humor, social norm, value assumption, or strategic positioning that works in one place but has no relevance, or produces the wrong reaction, in the target market. In these cases, preserving the original angle would reduce effectiveness or become meaningless.
Transcreation keeps the objective (e.g., motivate participation, build trust, increase engagement) but allows the message to be rebuilt using concepts and framing that resonate locally. The structure, examples, tone, and narrative approach may change substantially from the source.
In short:
The original framing does not work, hence the message must be reconstructed to achieve the desired outcome.
The best way to convey these concepts is through some real-world examples. Below are case examples from marketing, aerospace, and clinical practice and research.

TRANSCREATION IN PRACTICE
Transcreation becomes essential when the concept does not align with how a market thinks, speaks, or consumes.
CASE EXAMPLE 1: The iconic 'Thanda Matlab Coca-Cola' advertising campaign
When Coca-Cola re-entered the Indian market in the 1990s, it initially relied on its global positioning built around themes such as “Enjoy!” While effective in Western markets, that messaging did not resonate broadly across India, especially in rural regions where brand attachment was weaker and purchasing behavior differed from urban consumer patterns. Facing strong local competition, Coca-Cola realized that simply translating its global slogan will never secure meaningful market share.
Through the influence of its local campaign team, the company reframed its strategy around life in India. India’s intense summer heat and everyday language became the central themes. In colloquial Hindi, “thanda” means “cold” and is commonly used to refer generically to a cold drink (a “coolie”). By default, consumers did not ask for a brand name, they asked for a thanda. The campaign “Thanda Matlab Coca-Cola” (“Cold drink means Coca-Cola”) leveraged humor and culturally familiar storytelling to link the brand directly to relief from the heat. The brand’s main strategic objective – dominance in the soft drink category – remained constant around the globe, but the conceptual route to accomplish it shifted in India to align with local life and language.
The campaign reframed how the target market thinks about the brand. The shift in the message resonated so strongly with its target audience that more than 20 years later, Coca-Cola is still synonymous with ‘thanda’ across India.
That shift is a textbook example of transcreation. Learn more about this campaign from its director here.
CASE EXAMPLE 2: Phonemic Verbal Fluency (F-A-S)
Many neuropsychological assessment batteries designed to measure cognition include phonemic verbal fluency tasks such as:
“Name as many words as you can that begin with the letter F in 60 seconds.”
In English, the commonly used letter stimulus set (F-A-S) was selected because:
- The letters yield a comparable number of valid word candidates in the English lexicon.
- They produce manageable difficulty.
- They avoid excessive proper nouns or morphological bias.
However, this task cannot be directly transferred into many other languages, because:
- Letter frequency distributions differ.
- Phoneme–grapheme relationships differ.
- Some languages are syllabic rather than alphabetic.
- Some languages use non-Latin scripts.
- Some letters generate either too many or too few lexical options.
For example:
- In Spanish, F-A-S produces a very different word yield profile, hence P-M-R is its primary set.
- In Mandarin Chinese, there is no alphabetic letter-based retrieval that works the same way.
- In Japanese, kana-based syllabaries fundamentally alter retrieval mechanics.
- In Arabic or Hebrew, morphological root structures change how initial-letter constraints operate.
If you simply translate the instruction and keep the same letters, you change task difficulty. The test then no longer measures the same construct under comparable conditions.
In this case, translation and even transadaptation are insufficient.
The letter set itself must be reconstructed based on phonological frequency analysis in the target language. New letters, or syllabic units for different writing systems, must be selected to replace the approximate comparable lexical density, similar diffculty or equivalent executive retrieval demands.
Other examples include:
- Word-order manipulation tasks which are dependent on grammatical language structures.
- Language acquisition and development milestone measurements.
- Symbol translation tasks in IQ assessment.
- Symbol-Digit substitution tasks in IQ tests.
- Reading irregular words in dyslexia assessment batteries.
- Knowledge tests which are based on local educational curricula.
- Adaptive behavioral norms, and so on.
TRANSADAPTATION IN PRACTICE
Transadaptation becomes essential when the construct remains valid but the wording must be modified to protect it.
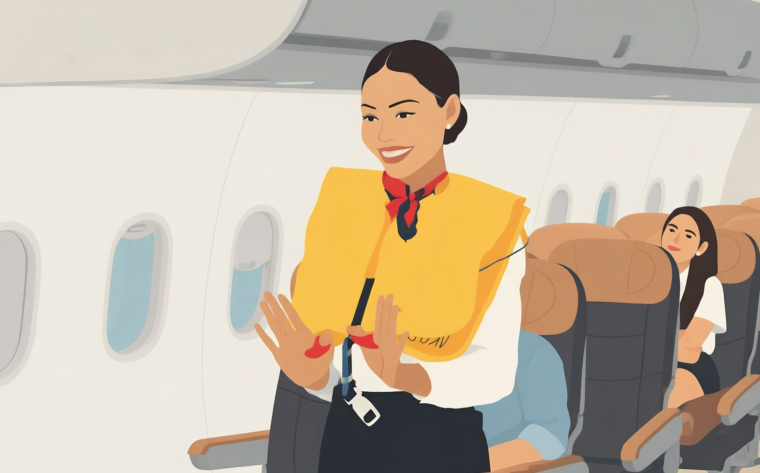
CASE EXAMPLE 1: Airline Safety Instructions
Consider a standard aircraft safety instruction:
“In the event of a loss of cabin pressure, oxygen masks will deploy automatically.
Pull the mask toward you and breathe normally.”
The safety concept is universal. Every airline must communicate the same procedure. The structure of the instruction remains stable across markets.
However, direct translation can introduce subtle but dangerous shifts in interpretation.
For example:
- “Deploy” does not have a natural equivalent in all languages and could be translated as “fall,” which changes the perceived mechanism and the passengers' expectations.
- “Pull the mask toward you” must clarify direction and action precisely in certain languages; literal phrasing may imply removing the mask instead of securing it.
- “Breathe normally” can be misinterpreted if the target language distinguishes between shallow breathing and calm breathing differently.
The concept does not change. The safety procedure does not change. Creative reframing is not necessary.
What changes is the phrasing needed to ensure that passengers interpret and execute the instruction correctly within their linguistic framework.
CASE EXAMPLE 2: Preserving Meaning in Clinical Symptom Reporting
Consider a patient questionnaire – a Patient-Reported Outcome measure (PRO) – that asks:
“Have you felt slowed down?”
In English, this phrase can capture psychomotor slowing, cognitive dulling, or generalized fatigue, depending on clinical context. The construct is intentionally broad.
In some languages, however, a literal translation of “slowed down” implies only physical immobility. In others, it may suggest laziness or lack of motivation. In still others, it may not exist as a natural expression at all.
If translated word-for-word, patients in different countries could interpret the question differently. That changes what is being measured. Consequently, the conceptual variation in their responses impact the interpretability and clinical meaning of collected data sets, and potentially influence diagnostic decisions.
The concept of psychomotor or cognitive slowing remains valid across cultures. But the phrasing must be adjusted to preserve that intended meaning. Transadaptation may involve clarifying the type of slowing, adjusting intensity markers, or selecting a culturally neutral expression that captures the same clinical nuance.
That is transadaptation.
LINGUISTIC COMPETENCE IN CROSS-CULTURAL ADAPTATION
Transadaptation and transcreation require a higher level of competence than standard translation. Fluency alone is insufficient. Both processes demand the ability to evaluate how meaning is constructed, how cultural context shapes interpretation, and how linguistic structure affects comprehension or performance.
For transadaptation, linguists must be able to:
- Detect when literal translation alters conceptual meaning.
- Distinguish semantic similarity from functional equivalence.
- Adjust phrasing, tone, or specificity without changing the underlying concept.
- Recognize connotative shifts that affect interpretation.
- Work within structured, documented decision frameworks.
In healthcare and clinical assessment contexts, this also requires sensitivity to construct and protecting its integrity. Minor wording changes can alter how a symptom is reported or how a behavior is interpreted. This work is analytical, disciplined and prioritizes precision over creativity.
Transcreation requires controlled creative competence. Linguists must be able to:
- Identify when the original framing will not resonate in the target culture.
- Reconstruct messaging to achieve the same objective.
- Adjust tone, metaphor, and narrative logic appropriately.
- Preserve strategic intent while modifying surface structure.
In cognitive and neurodevelopmental assessments, this may involve rebuilding test items when cultural or linguistic structure makes direct transfer impossible, while also preserving the construct being measured.
Transcreation requires high cultural intelligence, structural awareness, and strong judgment. The goal is to achieve the same action through culturally valid means.
DELIVERABLES AND FORMATS
Tranadapted and transcreated translation deliverables are provided in the same formats as all other translated materials. These are formats that support review, submission, publication, and institutional dissemination. Santium accepts the full range of common authoring and submission formats and can also support professionally formatted publication outputs when required.
Supported formats include:
- Editable documents (e.g., Word or equivalent) for author review, collaboration, and revision.
- Tabular formats (e.g., Excel) used for structured scientific content, tables, and reference materials.
- Structured and markup formats (e.g., XML, IDML or similar) used in publishing and content management workflows.
- Presentation formats for conference papers, posters, and academic dissemination.
In addition to translation, Santium offers multi-lingual graphic design and desktop publishing (DTP) services to support scientific content prepared for high-visibility use or professional publication. This includes handling layouts, adjusting space for longer or shorter texts after translation, switching from left-to-right text flows to right-to-left when required, adjusting figures, tables, references, and typographic conventions commonly required by journals, publishers, and institutional outlets.
Publication-ready outputs can be delivered in multiple formats suitable for professional production workflows, ensuring that translated content is structurally aligned and packaged with publication standards. This allows scientific materials to move directly from translation into submission or production without additional formatting steps.







Dedicated Translation Teams
Small project-specific multi-disciplinary groups.

Translation Experience
Training and experience in diverse translation domains.
ALIGNING WITH GLOBAL YOUR COMMUNICATIONS STRATEGY
DOMAIN-SPECIALIZED translators
Domain-specialized linguists support simple and complex translation across sciences, engineering, and business-related content, preserving intent, cultural relevance and sensitivity, terminology, tone, and brand alignment for clear, coherent global communication.
- 3,000+ translators and editors
- 140+ languages supported
- ISO-aligned, audit-ready workflows
- Follow-the-Sun project support across 14 countries
- Specialized dedicated project teams
STRENGTHEN YOUR LOCALIZED TRANSLATION
RELATED SERVICES
Already have translated corporate materials but aren’t sure they’re complete, localized, consistent, or up to date? Existing content can be reviewed to identify gaps, misalignment, or outdated language across medicine, sciences, engineering, technology, business, legal, financial, HR, or marketing materials. Missing content can be translated, earlier versions aligned, and existing assets updated, allowing you to build on what you already have instead of starting over.
SME Review & Editing
Subject-matter experts review translated content to assess accuracy, appropriateness, and alignment with the target market. SME review supports translation by validating contextual framing, phrasing, terminology, tone, and intent, resolving ambiguities, and strengthening confidence in materials used for governance, compliance, and high-visibility communication.


Linguistic Review & Editing
Linguistic reviewers refine translated content by correcting terminology, resolving unclear phrasing, and improving structure while preserving the original meaning. Editing focuses on clarity, flow, and accuracy so materials read naturally and meet professional communication standards across scientific, medical, and technical domains.
Glossary & Terminology
We build and maintain specialized terminology databases to unify language across subject-matter, studies and product lines. Controlled vocabularies reduce ambiguity, speed up editing time and strengthen quality assurance throughout the translation lifecycle.
Proofreading
Final quality checks address surface-level issues such as grammar, spelling, punctuation, formatting, and typographical errors. Proofreading ensures consistency and polish across related deliverables, supporting materials that are ready for publication, distribution, or formal submission.
Publication Support Writing
Scientific texts are prepared for publication through language and structural support that improves clarity, organization, and adherence to scholarly writing conventions. Writing support focuses on presentation and coherence while preserving the original scientific content, intent, and authorship.

Desktop Publishing
Scientific and technical content is formatted for clarity and consistency across multi-page documents, tables, and figures. Layout and typographic standards are preserved to maintain document integrity and readability, with outputs aligned to publication and institutional requirements.
Graphic Design
Scientific concepts, methods, and workflows are rendered into clear, professional visual formats, including presentations, figures, diagrams and culturally-observant illustrations. Design emphasizes accuracy, interpretability, and consistency to support effective scientific communication.
Our approach
The Santium method – where precision meets purpose
Santium’s methodology bridges linguistic accuracy with scientific discipline. Every project follows a validated, ISO-aligned process that preserves meaning, measurement, and usability across languages and contexts.
From concept review to pilot testing, each stage is designed to deliver traceable, reproducible outcomes in more than 140 languages worldwide.
Clients choose Santium for our ability to balance precision with understanding.
We adapt complex materials into content that communicates clearly and performs reliably, whether for regulators, clinicians, or patients, helping organizations build trust and consistency in their markets.
Multimedia and Digital Content Localization
For Training and Onboarding
Multimedia support includes subtitles, captions, and translated audio for training modules, e-learning programs, and presentations. Content such as SOP walk-throughs, protocol overviews, and procedural demonstrations is localized for clarity and usability across languages, helping global study teams deploy localized materials.

e-Learning Translation
High-quality translations for training content, learning modules, onboarding courses, and examination materials. Lessons, tests, and interactive elements are localized for clarity, usability, and cultural relevance, helping global study teams deliver consistent learning experiences across sites, languages, and user groups.

Video Subtitling & Closed Captions
Precise, well-timed subtitles and closed captioning support multilingual training content, including onboarding videos, e-learning modules, and SOP walk-throughs. Terminology and procedural language are translated clearly so multilingual teams can follow demonstrations with ease.

Voiceover Translation (Dubbing)
Transcription, subtitling, voiceover, script localization, video production, and UX review for multimedia used in multi-language training, recruitment and onboarding, education, and research.

Transcription
Accurate, polished and secure transcription for scientific, and technical content. Audio and video files are converted into clean, structured text that is ready for analysis, review, and multilingual adaptation. Ideal for e-Learning content, training materials, interviews, high-impact meetings, presentations and documentation needing archiving or long-term knowledge retention.

Software Localization
Software localization makes your digital content, screens, and user workflows feel native in every language. We adapt UI labels, messages, notifications, and task logic so they stay consistent and aligned with your requirements. Our team understands character limits, branching, scoring dependencies, and audit needs, delivering a seamless experience across devices.
Video Production
Video production for training and story-telling. We create clear, culturally relevant videos that simplify complex concepts and branding stories in many languages. Ideal for learning, onboarding, demonstrations, and enhancing comprehension and usability of scientific workflows.
Work with us
Partner with the experts in scientific, medical and technical translation
SIGN UP FOR UPDATES
KEEP IN TOUCH
|
|
Thank you for signing up. |


By submitting your email, you agree to receive occasional communications from Santium. You may unsubscribe at any time using the link in our emails. Your information will be processed in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
